|
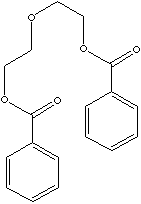
DIETHYLENE GLYCOL DIBENZOATE |
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 120-55-8 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 204-407-6 | |
| FORMULA | C18H18O5 | |
| MOL WT. | 314.34 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | 2,2'-Oxybis-, dibenzoate Ethanol; | |
| 2,2'-Oxydiethylene dibenzoate; Oxydiethylendibenzoat (Dutch); Dibenzoato de oxidietileno (Spanish), Dibenzoate d'oxydiéthylène (French); | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Clear viscous liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | 28 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 235 - 237 C at 7 mm Hg | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.175 - 1.180 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Slightly soluble | |
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| HENRY'S LAW |
|
|
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.5424 |
|
| FLASH POINT | 199 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Diethylene glycol dibenzoate, a glycol benzoate ester, is a clear liquid with chemically stable properties and high boiling point. It is slightly soluble in water and very soluble in polymers. It is used as a has an excellent compatibility with polyvinyl acetates and polyvinyl chloride. It is used as a plasticizer for PVA homopolymer and copolymer emulsions and as well as for PVC coatings, food packing adhesives and paints. It can be used as a softener in the field of cosmetics. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear to yellow liquid | |
|
ESTER CONTENT |
98.0% min |
|
| ACIDITY | 0.1% max | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.135 - 1.139 | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max |
|
|
HYDROXYL NUMBER |
15 max (mg KOH/g) |
|
|
COLOR, APHA |
100 max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 220 kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BENZOIC ACID |
||
|
Benzoic acid, the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid containing carboxyl group
bonded directly to benzene ring, is a white, crystalline organic compound;
melting at 122 C (starting sublime at 100 C); boiling at 249 C; slightly
soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, very slightly soluble in benzene and
acetone. Its aqua solution is weakly acidic. It occurs naturally in many plants
and resins. Benzoic acid is also detected in animals. The most of commercial
benzoic acid is produced by the reaction of toluene with oxygen at
temperatures around 200 C in the liquid phase and in the presence of cobalt and
manganese salts as catalysts. It can be prepared also by the oxidation of
benzene with concentrated sulphuric acid or carbon dioxide in the presence of
catalysts. Other methods are such as by the oxidation of benzyl alcohol,
benzaldehyde, cinnamic acid; by hydrolysis of benzonitrile, benzoyl chloride.
More than 90% of commercial benzoic acid is converted directly to phenol and
caprolactam. Its use in the production of glycol benzoates for the application
of plasticizer in adhesive formulations is increasing. It is also used in the
manufacture of alkyd resins and drilling mud additive for crude oil recovery
applications. It is used as a rubber polymerization activators and retardants.
Benzoic acid is converted to its salts and esters for the use of preservative
application in foods, drugs and personal products. Sodium benzoate, sodium salt
of benzoic acid, is used preferably as one of the principal anti-microbial
preservatives used in foods and beverages (but it's concentration is limited
usually not exceeding 0.1% because it is poisonous), as it is about 200 times
more soluble than benzoic acid. Sodium Benzoate is also used in medications,
anti-fermentation additives and tabletting lubricant for pharmaceuticals. The
industrial applications are as a corrosion inhibitor, as an additive to
automotive engine antifreeze coolants and in other waterborne systems, as a
nucleating agents for polyolefin, as a dye intermediate, as a stabilizer in
photographic processing and as a catalyst. Wide range of benzoic esters are used
as solvents, dying carrier, disinfectant additive, penetrating agent and
pesticides and manufacturing other compounds.
|
||